Select units of measurement for the temperature and rainfall tables (metric or imperial).
Average weather, temperature, rainfall, sunshine
Stretched over 3,700 kilometers (2,300 miles) from north to south, Argentina has a diverse range of climates, spanning from the
almost tropical climate of the north, to the
temperate climate of Buenos Aires and the Pampas, to the
cold and windy climate of Patagonia, and finally to the
subpolar climate of Tierra del Fuego. Moreover, there is the cold mountainous climate of the
Andes, arid in the northern and central part, and cold and snowy in the south.
Rainfall is abundant in the north-east, while snowfalls are frequent in the extreme south. In the south-central, in Patagonia, there is a vast arid area.
Being that it's located in the Southern Hemisphere, in South America, the seasons in Argentina are reversed in comparison with North America or Europe.
In the following map, we can see the
climate zones in Argentina.
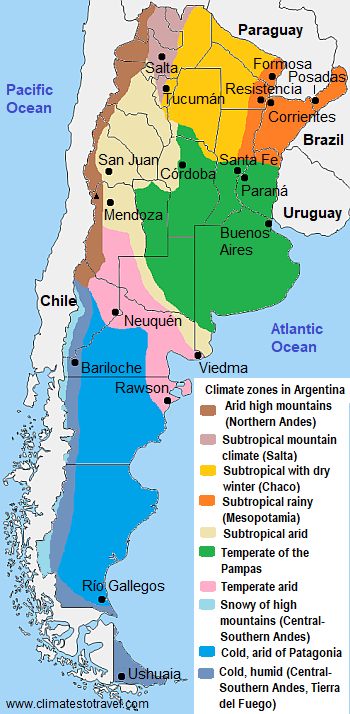
The climate in detail
Subtropical climate
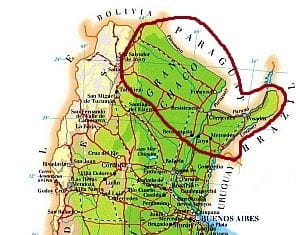
In the northernmost part of Argentina, the climate is subtropical, definitely hot in summer and pleasantly warm in winter. In the western part, the
Gran Chaco receives moderate rainfall, from 500 to 1,000 millimeters (20 to 40 inches) per year, with a pronounced dry period in winter. In this area, there are no big cities.
In
Las Lomitas, in the north, in the province of Formosa, the heat is intense from December to February, with average highs generally around 34/35 degrees Celsius (93/96 °F). The heat record is 46 °C (115 °F), among the highest in the entire South American continent. In winter, from May to mid-August, the daytime temperatures drop to around 24/25 °C (75/77 °F). However, the daily temperature range can be remarkable, so it can get hot even in winter, but it can sometimes get cold at night, especially when the
Pampero blows, i.e. the cold wind coming from the southern lands.
Rainfall in the Chaco is most abundant in the warm period, from November to March, when it occurs mainly in the form of showers and thunderstorms, while in winter it is rare. In summer, the sun shines quite often, despite the fact that it is the rainy season.
Further east, in the area that partially coincides with the "
Argentine Mesopotamia", delimited by the Paraná and Uruguay rivers, daytime temperatures are slightly lower, but rainfall is more abundant, and since it occurs quite frequently even in winter, there is no dry season.
In
Formosa, located in the northeast, on the border with Paraguay, the average temperature ranges from 17 °C (62.5 °F) in July to 28.3 °C (83 °F) in January.
However, the climate is much more humid and rainy. In fact, 1,405 millimeters (55 inches) of rain fall per year, and it can rain even in winter, albeit less than in summer: in July and August, respectively 40 and 35 mm (1.6 and 1.4 in) of rain fall on average.
Further south, we find the cities of
Resistencia and
Corrientes, which have a similar climate.

In the province of Misiones, east of Paraguay and of the Paraná River, the rains are even more abundant, so much so that this area is covered by forests.
In
Posadas, almost 1,900 millimeters (75 inches) of rain fall per year, at the
Iguazu falls (see
Puerto Iguazu), nearly 2,000 mm (78.5 in) per year, and in Oberá, as high as 2,300 mm (90.5 in). In this north-eastern portion, rainfall reaches or exceeds 100 mm (4 in) in all months, although it occurs mostly in the form of downpours or thunderstorms, and therefore does not compromise the amount of sunshine that much.
The highest flow of the waterfalls is recorded in the wettest period in the Iguazú River basin, that is, from November to March, while the lowest flow is recorded from August to October.
Humid temperate climate
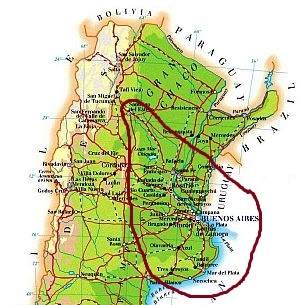
In this area, which is located to the south of the Gran Chaco, and includes the estuary of the Rio de la Plata River, the climate is
temperate, with mild winters and hot summers. Here the rainfall ranges from 500 to 1,200 mm (20 and 47 in) per year. Summer is moderately rainy everywhere because of afternoon showers and thunderstorms, while winter is rainy in the eastern part and drier in the western one. It follows that the rainiest part, the one with no dry season, is the eastern one, towards the sea and the border with Uruguay.
In
Buenos Aires, the capital of Argentina, the temperatures are reminiscent of the Mediterranean climate, the daily average ranging from 11.5 °C (52.5 °F) in July, with highs around 15 °C (59 °F), to 25 °C (77 °F) in January, with highs around 30 °C (86 °F). But in contrast with the Mediterranean climate, here
it rains in summer as well, although in the form of afternoon showers and thunderstorms, which do not decrease too much the sunshine duration.
Moreover, the
changes in temperature are bigger than in the Mediterranean because there are no obstacles to both cold air masses from the south (which may cause light frosts at night from May to September) and to warm air masses from the north, so much so that some days can be warm even in winter, with peaks of around 25/30 °C (77/86 °F).
Rainfall is well distributed throughout the year: there are 7/8 days with rainfall per month from October to April (when as mentioned, the rains mainly occur in the form of showers or thunderstorms) and 5/6 days per month from May to September. In the capital, it almost never snows: snow accumulation occurs a couple of times per century.

The
sea in much of Argentina is cool to swim in. In fact, on the eastern side of South America, a cold current, known as the Falkland Current, flows up to the latitude of
Mar Del Plata, where the sea temperature reaches 20 °C (68 °F) in February and 19 °C (66 °F) in January and March. It goes better in Buenos Aires, where the sea is warm enough for swimming in January and February.
In
Rosario, 270 kilometers (168 miles) north-west of Buenos Aires, the weather is similar to that of the capital, although with greater temperature variations between night and day.
In
Córdoba too, the average temperatures are quite similar to those of Buenos Aires, since the city is located north of the capital but also farther from the sea and at 470 meters (1,500 feet) above sea level. However, the diurnal temperature range in Cordoba are higher than in the capital, and the winter is definitely drier. The average temperature ranges from 10 °C (50 °F) in July to 24 °C (75 °F) in January.
Arid climate
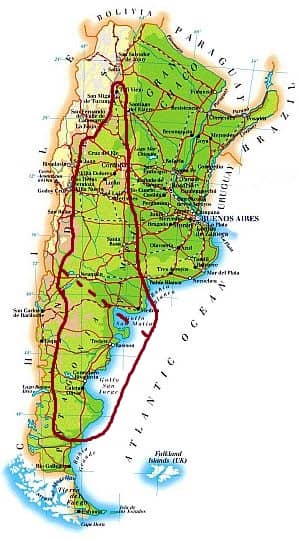
In this vast area, encompassing the western and arid part of the Pampa (above the dashed line) and most of Patagonia (south of the dashed line), the climate is
arid, semi-arid or desert. This happens both because of the distance from the sea and because of the Andean chain, which blocks humid winds coming from the Pacific (the southern part the Atlantic coast is arid as well because at these latitudes the westerlies prevail, and also because in the sea a cold current flows, which reduces evaporation).
Clearly, the temperatures vary with latitude, but some features remain similar: the
temperature range between night and day is usually considerable (particularly in areas distant from the sea); the
wind, either cold or hot, can sweep the vast plains, and it's also capable of causing dust storms; temperature variations can be considerable. The sun frequently shines in summer, while in the coldest period, from May to September, the sky can be cloudy.
In
Mendoza, located at 700 meters (2,300 feet) above sea level, at the foot of the Andes and not far from Mount Aconcagua, the daily average temperature ranges from a low of 8.5 °C (47.5 °F) in July to a high of 26 °C (79 °F) in January. During the day, the temperature may reach or exceed 30 °C (86 °F) even in winter, while at night, it can slightly drop below freezing from April to September.
In Mendoza, only 240 mm (9.5 in) of rain fall per year, with a maximum in summer, between December and March.
Patagonia
Patagonia, the southern region of Argentina (as well as of Chile), begins approximately at the 40th parallel, and most of it is located in the arid climate zone we are dealing with here, but at this latitude the weather is more
cool and windy. The winds are often strong and are able to increase the feeling of cold.
In
Trelew, on the Atlantic coast at the 43rd parallel south, the average temperature goes from 21.5 °C (70.5 °F) in January to 6.5 °C (43.5 °F) in July. In summer, brief heat waves can occur, with peaks above 37 °C (99 °F). The sun often shines from November to March.
Here it rains very little, just 220 millimeters (8.7 in) per year, and in fact the landscape is semi-desert, without trees and with some xerophilous shrubs. In winter, however, it can snow and freeze.
In Trelew the sea is cold, in fact it barely reaches 17 °C (63 °F) from January to March (so it is not recommended for swimming), and hits a low of 9.5 °C (49 °F) in August and September.
A little further north, in
Puerto Madryn, and even further south, still on the coast, in
Comodoro Rivadavia, the climate is similar.

Tierra del Fuego
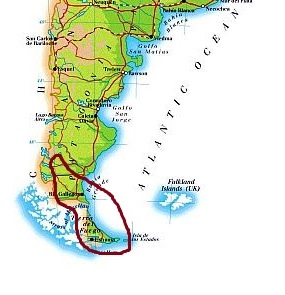
In the southernmost part of Patagonia and in Tierra del Fuego, the climate is
cold oceanic, that is, with average temperatures close to freezing in winter and around 10 °C (50 °F) in summer (or even subpolar where the average in summer drops below this value, as happens in the
Isla de los Estados). Precipitation, which at this latitude often occurs in the form of snow, is higher than in the arid zone, both because at this latitude the Andes in the west are definitely low (therefore the humid currents from the Pacific Ocean can penetrate inland) and because this region can be affected by
cold and wet winds from the nearby Antarctic Ocean.
Winter is not freezing: it is true that there may be cold spells, in which the temperature can drop to -15 °C (5 °F), but they are usually replaced after a few days by the westerlies, which are less cold. However, the wind almost constantly blows, which can increase the feeling of cold.
Anyway, in the coldest locations, such as
El Calafate and
Río Grande, the average temperature in June and July is very close to the freezing point.
In
Ushuaia, located on the coast and at a latitude of 54 degrees south, the average in June and July is just 2 °C (36 °F), while in summer, the average reaches 10.5 °C (51 °F) in January and February. At night, the temperature can drop below freezing throughout the year: to -1/-2 °C (28/30 °F) between December and February, and to as low as -10/-12 °C (10/14 °F) from June to August.
Rainfall is frequent in summer as well as snowfall in winter, although the amount is not high, around 450 mm (17.5 in) per year. The sky is often cloudy, so the sun is seen quite rarely all year round.
In Tierra del Fuego, the sea is cold all year round, and reaches a maximum of 9 °C (48 °F) in February and March.

Andes
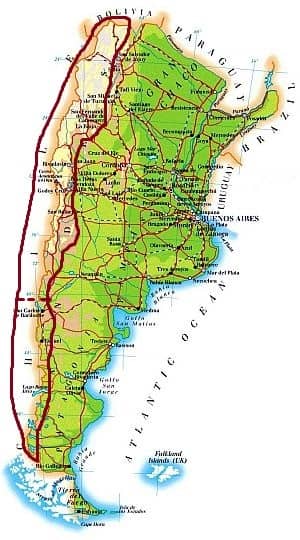
In the very long Andean band, which crosses Argentina in the western part from north to south, the climate becomes progressively colder with increasing altitude, but also with latitude: the more you go to the south, the lower the temperature at a given altitude, and the lower the height in which eternal snows begin.
The Andean zone can be divided into two distinct areas, separated by the dotted line on the map. North of the 40th parallel, the climate is arid, while south of this latitude, it is Alpine, and snowfalls can be abundant.
In the
central and northern provinces, the Andes are
arid at high altitudes, in fact they are desert also on the western side, i.e. in Chile, so there is no moisture that might pass over the ridge.
In the northern Andes, from November to March there can be some rain or thunderstorms, and above 3,700 meters (12,000 feet, see El Aguilar, Tres Cruces), in the coldest hours of the morning it can even snow, even if it is summer. However, snow is more frequent at higher altitudes, and in fact you have to climb the rare peaks above 6,000 meters (19,700 feet), like Nevado Queva, to find some
snowfields, where snow remains on the ground because of the cold.
Above 3,000 meters (10,000 feet), during the cold and dry period, from April to October, intense frosts can occur at night, but during the day, when the sun shines, the temperature goes above freezing, so the daily temperature range is remarkable (see
La Quiaca). This happens because at high altitudes, at subtropical or tropical latitudes, the sun is very strong.
In the northernmost area, where cities such as Jujuy, Salta and Tucumán are located, below 2,000 meters (6,500 feet), the rains increase because moisture comes from the eastern plain.
In
Salta, which is located almost at the Tropic, at 1,200 meters (4,000 feet) of altitude and west of the Gran Chaco, the average temperature ranges from 11.5 °C (52.5 °F) in June to 22 °C (72 °F) in January. So, the climate at this latitude is mild even at 1,200 meters (4,000 feet), although there may be slight frosts at night from May to September.
In Salta, 750 mm (29.5 inches) of rain fall per year, but it almost never rains from May to September, although at this time the sky is often overcast. Rainfall occurs from December to March, usually in the form of downpours or thunderstorms, which don't reduce too much the summer sunshine.
North of Salta,
San Salvador de Jujuy has a similar climate.

In Argentina, there are several very high peaks, among which
Aconcagua, located in the central part, which is the highest mountain in the entire American continent with its 6,962 meters (22,841 feet). At the latitude of Aconcagua (32 degrees south), we find perennial snows above 4,000 meters (13,000 feet), while in the area of Cerro Torre (around 49 degrees south), they begin at 1,500 meters (5,000 feet), although the Viedma Glacier, which enters in the lake of the same name because of gravity, comes down to just 250 meters (800 feet). In the extreme south, eternal snows are found above a few hundred meters (a thousand feet) of altitude.
At the latitude of Mount Aconcagua, at high altitudes,
precipitation (which in this area is more frequent in winter and therefore is generally in the form of snow) amounts to about 250/300 mm (10/12 inches) per year, like in semi-desert climates. You have to go to Patagonia, more or less at the 40th parallel south (which, as mentioned, is indicated by a dotted line on the map) to find some greenery along the Andean slopes of Argentina.
In this area located south of the 40th parallel, where the climate is
arid in the plains and humid in the mountains, the cities at the foot of the mountains are quite rainy even where to the east there's a desert. In addition, the wind coming down from the mountains (called
zonda and similar to the
chinook of the Rocky Mountains or to the
föhn of the Alps) can cause rapid increases in temperature.
In
San Carlos de Bariloche, located at 41 degrees latitude south and 850 meters (2,800 feet) above sea level, the average temperature ranges from 2.5 °C (36.5 °F) in July to 15 °C (59 °F) in January and February.
In Bariloche, 800 mm (31.5 in) of rain (or snow) fall per year, while 200 km (125 miles) to the east, in Maquinchao, precipitation drops to 200 mm (8 in).

On
Cerro Catedral, 2,400 meters (7,800 feet) above sea level and not far from Bariloche, the average temperature drops below freezing from June to September, and reaches 7.5 °C (45.5 °F) in January. The wind is often strong throughout the year. Snowfalls during winter are abundant, but sometimes it can snow even in summer. In this area, the landscape reminds that of the Alps, and there are renowned ski resorts, where you can go skiing when in North America or Europe it's the summer.
In the southern Andes, there are vast glaciers and lakes of glacial origin, whose banks have the same shape as the fjords.
When to go
It is not easy to find a single period in which the weather is very good throughout the country. However, since in the extreme south the best period is
the austral summer, from December to February, you can choose this period for the rest of the country as well, keeping in mind that at this time, in the north it will be very hot. All in all,
November, a spring month, can also be a good compromise for most of the country, although in the far north, it can already be a hot month.
To visit the
north (see the Chaco, Formosa, Puerto Iguazú), since the main purpose should be to avoid the heat (either the intense but dry heat of the west or the sultry heat of the east), you can choose the
winter, from May to August, keeping in mind that it can sometimes get cold at night, that in the east sometimes it can rain, and that the sky may be cloudy.
The best times to visit the
north-central (see Buenos Aires, Rosario, Córdoba) are
spring and autumn (October-November and March-April), although there may be periods of bad weather and sudden changes in temperature. In Buenos Aires, the best time is usually spring, from late September to early December.
The best time to visit the
extreme south (Tierra del Fuego) is
summer, from December to February: temperatures are cool, even cold at night, but tolerable, at least when the wind doesn't blow.
In the mountain resorts, located mostly in the center-south of Argentina (but some also in the extreme south), the
ski season normally runs from July to September.
What to pack
In
winter (June to August): in the north, at the Iguazu Falls and in the Gran Chaco, bring clothes for spring and autumn (light for the day), a sweatshirt or sweater and a jacket for the evening. In the center-north and in Buenos Aires, bring warm clothes, such as a sweater, a jacket, and an umbrella. In Patagonia and Tierra del Fuego, bring very warm clothes, such as a down jacket, a warm hat, gloves, a scarf, a rain jacket, and comfortable shoes. In the Andes: in the northern part, clothes for spring and autumn for the day, a warm jacket and a hat for the evening, sunscreen and sunglasses; in the southern part, warm clothes, such as a down jacket, a scarf, gloves, and hiking boots.
In
summer (December to February): in the north, at the Iguazu Falls and in the Gran Chaco, bring lightweight clothing of natural fibers, a light sweater and a light raincoat for thunderstorms, and a sun hat. In the center-north and in Buenos Aires, bring summer clothes, a sweatshirt for the evening, and possibly a light raincoat for thunderstorms. In Patagonia, clothes for spring and autumn, a jacket for the evening, a sweater, and comfortable shoes. In Tierra del Fuego, warm clothes, such as a sweater, a raincoat, a jacket, and boots; be ready to remove the outer layer in mild days. In the Andes: in the northern part, clothes for spring and autumn during the day, a warm jacket for the evening, sunscreen and sunglasses; in the southern part, a down jacket, a scarf, gloves, and hiking boots.
Climate data - Argentina
| Bariloche (850 meters) |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 7 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 1 | 0 | -2 | -1 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 23 | 23 | 20 | 15 | 11 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 |
|---|
| Precip. | 25 | 20 | 30 | 55 | 115 | 170 | 125 | 115 | 55 | 50 | 30 | 25 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 4 |
|---|
| Humidity | 48% | 49% | 56% | 65% | 74% | 78% | 76% | 72% | 63% | 57% | 52% | 50% |
|---|
| Day length | 15 | 14 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
|---|
| Sun hours | 11 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 11 |
|---|
|
| Buenos Aires |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 20 | 19 | 18 | 14 | 11 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 13 | 16 | 18 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 30 | 29 | 27 | 23 | 19 | 16 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 23 | 26 | 29 |
|---|
| Precip. | 135 | 130 | 120 | 130 | 95 | 60 | 75 | 70 | 80 | 125 | 120 | 125 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 7 |
|---|
| Humidity | 63% | 66% | 69% | 73% | 78% | 75% | 74% | 69% | 68% | 68% | 62% | 61% |
|---|
| Day length | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 14 |
|---|
| Sun hours | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|
| Sea temp | 22 | 23 | 22 | 19 | 16 | 14 | 12 | 12 | 13 | 15 | 18 | 21 |
|---|
| Formosa |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 22 | 22 | 21 | 18 | 15 | 13 | 12 | 13 | 15 | 18 | 19 | 21 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 34 | 33 | 32 | 29 | 24 | 23 | 23 | 25 | 27 | 30 | 31 | 33 |
|---|
| Precip. | 165 | 135 | 140 | 160 | 110 | 60 | 40 | 35 | 75 | 150 | 160 | 180 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 8 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
|---|
| Humidity | 69% | 72% | 74% | 77% | 79% | 79% | 74% | 67% | 66% | 70% | 68% | 69% |
|---|
| Day length | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 |
|---|
| Sun hours | 9 | 8 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|
|
| Las Lomitas |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 22 | 22 | 20 | 18 | 14 | 12 | 11 | 13 | 15 | 19 | 20 | 21 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 36 | 34 | 33 | 29 | 25 | 24 | 24 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 33 | 35 |
|---|
| Precip. | 130 | 120 | 155 | 95 | 65 | 15 | 15 | 10 | 25 | 70 | 130 | 130 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 7 | 7 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 6 | 7 | 7 |
|---|
| Humidity | 62% | 68% | 71% | 75% | 74% | 73% | 65% | 54% | 55% | 58% | 61% | 64% |
|---|
| Day length | 14 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 |
|---|
| Sun hours | 8 | 7 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 7 |
|---|
|
| Mendoza (750 meters) |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 19 | 18 | 16 | 11 | 7 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 15 | 18 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 33 | 31 | 28 | 23 | 19 | 16 | 15 | 19 | 22 | 26 | 29 | 32 |
|---|
| Precip. | 45 | 40 | 30 | 20 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 25 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 4 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
|---|
| Humidity | 46% | 51% | 57% | 61% | 65% | 63% | 58% | 49% | 45% | 43% | 41% | 42% |
|---|
| Day length | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 14 |
|---|
| Sun hours | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|
|
| Puerto Iguazu |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 21 | 20 | 19 | 17 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 17 | 18 | 20 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 32 | 32 | 31 | 28 | 24 | 22 | 22 | 25 | 27 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
|---|
| Precip. | 180 | 150 | 155 | 160 | 185 | 145 | 105 | 85 | 155 | 245 | 170 | 220 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 9 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 8 | 11 | 8 | 10 |
|---|
| Humidity | 77% | 79% | 79% | 82% | 86% | 87% | 83% | 76% | 75% | 77% | 74% | 76% |
|---|
| Day length | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 |
|---|
| Sun hours | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 6 |
|---|
|
| Salta (1,150 meters) |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 17 | 16 | 15 | 12 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 8 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 28 | 26 | 25 | 23 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 23 | 25 | 27 | 28 | 28 |
|---|
| Precip. | 195 | 145 | 105 | 40 | 10 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 25 | 60 | 140 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 12 | 11 | 10 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 7 | 10 |
|---|
| Humidity | 76% | 78% | 81% | 80% | 78% | 71% | 64% | 55% | 52% | 58% | 64% | 70% |
|---|
| Day length | 14 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 13 | 14 |
|---|
| Sun hours | 6 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
|---|
|
| Trelew |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 14 | 13 | 11 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 7 | 10 | 12 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 29 | 28 | 25 | 21 | 16 | 13 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 25 | 28 |
|---|
| Precip. | 10 | 25 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 20 | 15 | 15 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
|---|
| Humidity | 39% | 46% | 49% | 53% | 62% | 65% | 63% | 55% | 52% | 46% | 41% | 39% |
|---|
| Day length | 15 | 14 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 15 | 15 |
|---|
| Sun hours | 10 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 9 |
|---|
| Sea temp | 17 | 17 | 17 | 15 | 13 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 13 | 15 |
|---|
| Ushuaia |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 6 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 14 | 14 | 13 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 8 | 11 | 13 | 14 |
|---|
| Precip. | 45 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 35 | 40 | 35 | 40 | 30 | 30 | 40 | 45 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 9 | 8 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 9 | 9 |
|---|
| Humidity | 69% | 72% | 73% | 76% | 78% | 80% | 79% | 76% | 72% | 68% | 68% | 69% |
|---|
| Day length | 16 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 17 |
|---|
| Sun hours | 5 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
|---|
| Sea temp | 9 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|
See also the
temperatures month by month