The climate of Indonesia is almost everywhere
equatorial, ie hot, humid and rainy throughout the year. However, in some areas, there is a dry season, more or less marked, and therefore the climate can be defined as sub-equatorial or
tropical.
As usually happens in hot countries, the rains occur in the form of downpours or thunderstorms, which sometimes can cause flooding.
There are also
mountains and volcanoes, often very high, where the temperature naturally decreases with altitude.
Being that Indonesia is located near the Equator, the day lasts 12 hours throughout the year, and the sun sets quite soon. However, the sun's rays are very strong, especially in the mountains.
The
temperature is stable, with lows around 22/25 °C (72/77 °F) and highs around 30/32 °C (86/90 °F) all year round.
The main difference is found in the
rainfall, whose quantity and distribution are due to the location in a hot and humid area, but also to the
monsoon regime, and the impact that it has on the different areas. The northwest monsoon takes place from December to March, and the southeast monsoon from June to September. These winds have a different impact depending on the presence of mountains and on slope exposure. However, the rains do not always follow the same pattern from year to year, as we will see when dealing with El Niño.
Indonesia is a vast archipelago made up of
thousands of islands, stretching along the Equator from Southeast Asia to Australia: it covers more than 5,000 kilometers (3,000 miles) from west to east, a distance similar to the one found between the west and east coasts of Canada. Some consider the Papua province (Western New Guinea) as part of Oceania, and in this case, Indonesia would be a transcontinental country.
The climate in detail
Equatorial climate
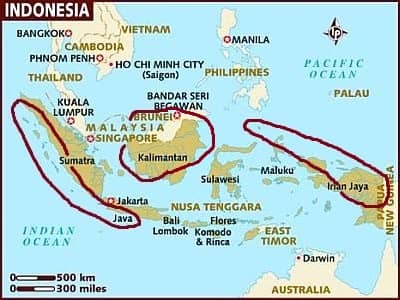 Indonedia, areas with an equatorial climate
Indonedia, areas with an equatorial climate
The climate is equatorial, with
abundant rainfall throughout the year, in the following areas: the western coast and the western side of Sumatra, the southern side of western Java, almost all of Borneo (except the south-east) and much of Western New Guinea (formerly Irian Jaya).
Here, it is difficult to find a best time to visit.
The southwestern coast of
Sumatra is very rainy. Here, from 3,000 to 4,000 millimeters (120 to 155 inches) of rain fall per year, and it is difficult to find an acceptable period. The worst period goes from October to December, when rainfall exceeds in certain areas 400 mm (16 in) per month.
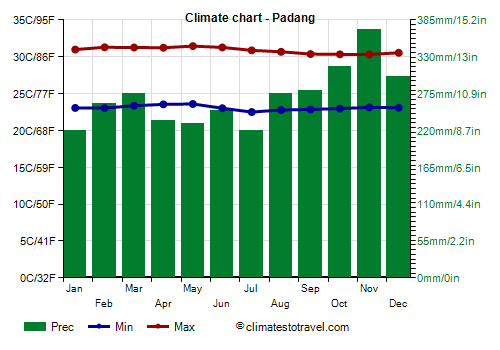
![]() Climate chart - Padang
Climate chart - Padang
The only city of some importance in this area is
Padang, which is relatively less rainy in June and July, although the decrease in precipitation does not occur every year.
 Padang
Padang
Off the south-west coast of Sumatra, we find the Mentawai Islands.
The island of
Borneo (in the Indonesian part, called Kalimantan) is mostly very wet and covered with an impenetrable rainforest. In the wettest regions, i.e. the inland area and the north-east, it is difficult to find a month when the rainfall is below 250 mm (10 in). However, the (relatively) least rainy period generally runs from June to August.
In
Pontianak, on the west coast of Borneo, the maximum temperature fluctuates between 31.5 °C (89 °F) in December and 33 °C (91.5 °F) in May. On average, 2,900 mm (14 in) of rain fall per year, with a maximum between October and December. The amount of sunshine is not very good, as it often rains all year round.
The northern part of the Moluccas (Maluku Islands) and the center-north of Western New Guinea have also an equatorial climate. Here, it usually rains relatively less from July to October.
Sub-equatorial climate
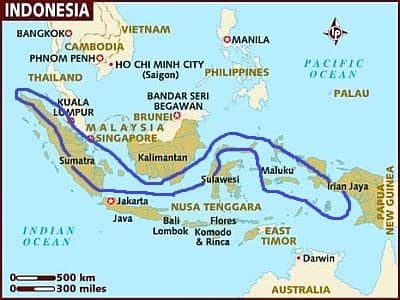 Indonesia, areas with a sub-equatorial climate
Indonesia, areas with a sub-equatorial climate
In this area (comprising the interior and the northern side of Sumatra, south-eastern Borneo, the northernmost tip of Sulawesi, the north-central Maluku islands and the westernmost part of New Guinea), the climate can be considered sub-equatorial, since there is no real dry season, but there's a time of the year when the rainfall becomes less abundant, that is, around 100 mm (4 in) per month. This least rainy period is therefore the one to be preferred, however, it's not the same everywhere.
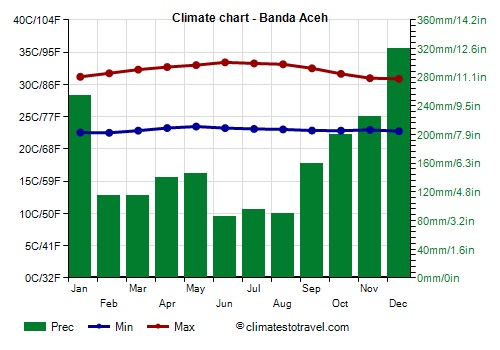
![]() Climate chart - Banda Aceh
Climate chart - Banda Aceh
In the northern part of the island of Sumatra, in
Banda Aceh, almost 2,000 mm (80 in) of rain fall per year. Here the wettest period is from September to January, with more than 150 mm (6 in) per month, then there is a secondary peak in the rains in April and May.
So, here we have two relatively dry periods,
from June to August, when precipitation drops below 100 mm (4 in) per month, and
from February to March, when it is around 115/120 mm (4.5/4.7 in) per month. The worst month is December, with as much as 320 mm (12.6 in).
The amount of sunshine is not great all year round, however, it is slightly better from February to July, and worse in November and December.
There sultry weather throughout the year, but the breezes temper a bit the heat, especially from June to August.
A little more to the south, but still on the north coast of Sumatra, in
Medan too, around 2,000 mm (80 in) of rain fall per year, but precipitation is more evenly distributed over the seasons. Here the best months are
February and March, but also
June and July, while the rainiest period begins already in August, and lasts until December.
In Medan too, the weather is hot and muggy throughout the year, and the breeze is less lively than in Banda Aceh.
Borneo is rainy throughout the year, but in the south-east (see
Banjarmasin), there's a relative decline between June and October, when the rains, however, still hover between 100 and 150 mm (4 and 6 in) per month.
On the northern side of
Sulawesi (see Manado), the rainfall has a relative decrease from July to September, when it amounts to about 110/140 mm (4.3/5.5 in) per month.
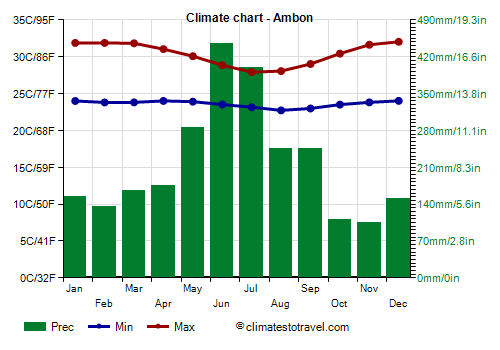
![]() Climate chart - Ambon
Climate chart - Ambon
The
Central Malukus, on islands such as Buru,
Ambon and Seram, experience a reversed rainy season, so they are very rainy from May to September, especially in June and July, when they can receive more than 400 mm (16 in) of rain per month, while the least rainy period runs from October to February, when, however, precipitation still exceeds 100 mm (4 in) per month. This rainfall pattern is also observed at the western tip of Papua, around Sorong.
Tropical climate
 Indonesia, areas with a tropical climate
Indonesia, areas with a tropical climate
In this area of Indonesia, the climate can be defined as tropical because there is
a period with moderate or even poor rains, from June to September, due to the southeast monsoon. So, here it is possible to find a best period, at least as regards to the rains, while the heat can be intense anyway.
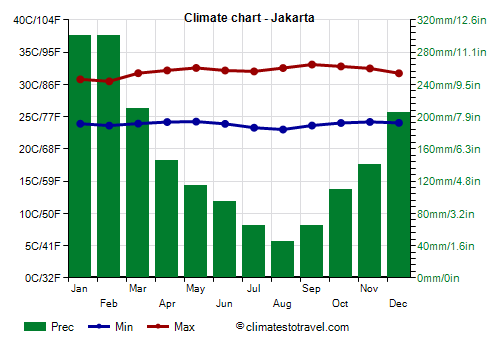
![]() Climate chart - Jakarta
Jakarta
Climate chart - Jakarta
Jakarta, the capital of Indonesia, is located on the north side of Java. Here, the weather is hot and humid, with stable temperatures all year round. Owing to the so-called urban heat island effect, the heat is more intense within the big city, while sea breezes bring a bit of relief especially in the neighbourhoods close to the coast. The temperature rarely drops below 20 °C (68 °F) at night, while sometimes it can reach 35/36 °C (95/97 °F) during the day.
Rainfall amounts to 1,800 mm (70 in) per year; the rains are abundant from December to March, with a maximum of 300 mm (12 in) in January and February. The driest period, which is therefore the one to be preferred, is from June to September.
In Jakarta, the sun often shines in the long period when it does not rain a lot, from April to October. On average, there are nearly 3,000 hours of sunshine per year.
 Jakarta
Jakarta
In
Bandung too, there is an evident dry season. Moreover, being located at 700 meters (2,300 feet) above sea level, this city has also a milder climate, with highs around 28/30 °C (82/86 °F) and lows around 18/20 °C (64/68 °F). Here, the best period is from July to September, and the driest month is August, with an average of 50 mm (2 in) of rain. Here are the average temperatures.
Semarang is located on the northern coast of Java, east of Jakarta. Here the wettest month is January, with up to 430 mm (17 in) of rain, while the best period is from June to August; September has still little rain, but it is hotter. In fact, in this as in other parts of Indonesia, there is a slight increase in temperature in September and October.
The eastern part of Java is not as rainy as the western one. In
Surabaya, a hot and sunny city, 1,750 mm (70 in) of rain fall per year, with a maximum of more than 200 mm (8 in) per month from December to March; on the other hand, little rainfall occurs from July to September, and around 50/60 mm (2/2.4 in) in June and October.
Considering the heat that is intense especially in September and October, the best period here is from
June to August.
Bali and eastern islands
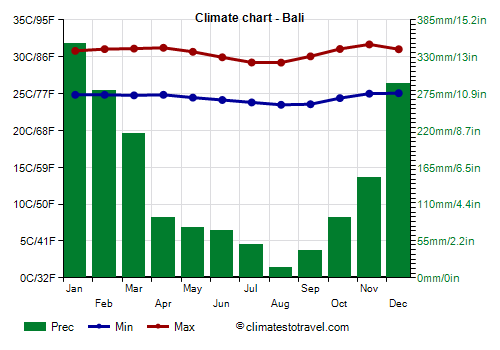
![]() Climate chart - Bali
Climate chart - Bali
We find a similar situation on the island of
Bali, located east of Java. Here, 1,700 mm (67 in) of rain fall per year, the heat is less intense than in big cities because of the breeze, and all in all, the best period is from June to September.
 Bali
Bali
 Eastern Islands, where they are located
Eastern Islands, where they are located
East of Bali (see
Lombok,
Sumbawa,
Komodo,
Flores,
Sumba), the dry season is longer, and the rainfall decreases further, to around 1,300/1,400 mm (51/55 in) per year along the coasts (while it remains higher in inland areas, especially where there are highlands, as happens for example in Ruteng, on the island of Flores, where it rains a lot from October to April). On the southernmost islands of the Lesser Sunda Archipelago (or Nusa Tenggara), such as in Sumba, precipitation is even scarcer and drops below 1,000 mm (40 in) per year. Here, the driest period, which is very pronounced, is from May to November, even though it's definitely hot between September and November.
 Lasiana beach, Timor
Lasiana beach, Timor
On the island of
Timor, from 1,200 to 1,500 mm (47 to 60 in) of rain fall along the coast; in August and September, the rains are poor, but in general, they are acceptable from May to October. Some areas of the island are semi-arid.
East of Timor, on the
southern Malukus (Banda, Tanimbar, Kai, Aru), the rainfall is more abundant, and it surpasses 2,000 mm (80 in) per year, but there is still a dry season, though a little shorter, from
August to October. For example, in
Tual, on the Kai Islands, 2,600 mm (102 in) of rain fall per year, with heavy rains from December to May, 110 mm (4.3 in) in July, and less than 100 mm (4 in) per month from August to October.
In the southwestern part of the island of Sulawesi (Celebes), in
Makassar (Ujung Pandang), it rains a lot, more than 400 mm (16 in) per month, from December to March, with a peak of as high as 700 mm (27.5 in) in January, but rainfall drops below 100 mm (4 in) per month from June to September.
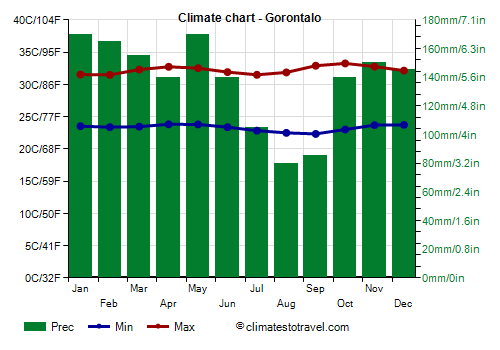
![]() Climate chart - Gorontalo
Climate chart - Gorontalo
In other areas of Sulawesi, precipitation drops below 2,000 mm (80 in) per year. In the center-north, in
Luwuk, there is no month with very abundant rainfall: the rainiest month is March, with 155 mm (6.1 in), while the rainfall drops below 70 mm (2.8 in) in September and October. In
Gorontalo, the least rainy months are August and September, while the rainiest is May, with about 170 mm (6.7 in). We are in a fairly sheltered area, which also includes the Gulf of Tomini and the
Togian Islands, where there is a coral reef which that invites you to go diving.
In south-eastern Sulawesi, precipitation drops below 2,000 mm (80 in) per year as well; in
Kendari, it drops below 100 mm (4 in) per month from August to November. In the
Wakatobi archipelago, an acronym for the islands of Wangi-wangi, Kaledupa, Tomia, and Binongko, rainfall is quite rare from July to October.
In the southernmost part of
New Guinea, in South Papua Province (see
Merauke), there is a clearly defined period of little rain from June to October.
Sea temperature
The
sea in Indonesia is warm enough to swim in all year round, with little temperature variations between the months. In some sea areas, such as the straits of Sape and Lombok, there can be strong currents, while in others, it's useful to mention the presence of sharks.
Mountains
In Indonesia, there are several mountain ranges. The island of Java is dotted with volcanoes; the highest peak, however, is in Western New Guinea:
Puncak Jaya, belonging to the Maoke Mountains, is 5,000 meters (16,400 ft) high, and despite its position near the Equator, it is home to some snow fields around the top which, however, are in retreat because of global warming.
In the areas near the mountains, there's a higher risk of
showers and thunderstorms: Bogor, near Jakarta, is the city with the highest number of days with thunderstorms in the world, as many as 322 per year! The rains are more abundant along the
windward sides, that is, along the northern slopes during the northwest monsoon (December to March), and the southern slopes during the southeast monsoon (June to September).
The temperature naturally decreases with altitude, but cold weather is only found at high altitudes.
In
Wamena, New Guinea, 1,650 meters (5,400 feet) above sea level, the average daily temperature is around 19/20 °C (66/68 °F) all year round.
At 2,500 meters (8,200 ft), the daily average is around 15 °C (59 °F), and at night it gets cold.
Cyclones
Almost all of Indonesia, being near the Equator, is not in the path of
tropical cyclones. However, the southernmost areas, and more rarely the northernmost ones, can be affected by them.
- The
southern islands (Java, Bali, Sunda Islands, Timor, southern New Guinea), can be affected by the Southern Hemisphere cyclones, between November and May (but more likely, between December and mid-April). Generally, Java and Bali are not directly affected, while the southeastern islands (Flores, Sumba, Timor, Savu, Rote, southern New Guinea) can be. Cyclones, when they don't directly hit a particular area with their load of rain and wind, can still cause damage to tourist facilities because of abnormal waves.
- On the other hand, north of the Equator, the island of
Sumatra, especially in the northernmost part, can be affected by cyclones when they are in the early stages of their formation in the Andaman Sea or in the Bay of Bengal, or it can be affected in a more marginal way by the typhoons that come from the Pacific and pass over the Gulf of Siam. In this case, cyclones are formed from April to December, with two peaks at the beginning and at the end of the period (so, in April-June and October-December). However, given the warm sea, they can, in theory, form all year round.
El Niño
In addition, the climate in Indonesia is influenced by the phenomenon known as
El Niño, which brings
drought, as well as an
increase in air and sea temperature, an event which may cause coral bleaching.
The drought caused by El Niño is pronounced between June and August, and even more so between September and November; owing to this phenomenon, the fires that are usually lighted during the dry season can become uncontrollable, and cause the spread of smoke in large areas.
The opposite phenomenon,
La Niña, brings more rains than usual, as well as temperatures cooler than usual between June and August.
When to go
Generally, the best time to visit Indonesia runs from
June to September, since it is the driest time of year in areas with a tropical climate.
However, there are areas where the situation is different, especially the central Malukus, which in this period receive the highest amount of rainfall of the year, while they are less rainy from November to February. Furthermore, in areas with an equatorial climate it rains a lot all year round.
For a
beach holiday, the most suitable areas are those with a tropical climate, choosing of course the least rainy period.
What to pack
All year round: bring
tropics-friendly, loose-fitting clothing, a scarf for the breeze, and a light sweatshirt for air-conditioning. You can add a light raincoat or an umbrella, in areas with an equatorial climate all year round, and in areas with a tropical climate during the rainy season.
In Bandung, around 1,000 meters (3,300 feet), you can add a sweatshirt and a light jacket; in high mountains, bring warm clothes, a warm jacket, a raincoat, and hiking shoes.
When going to the reef, you can bring snorkeling equipment, including water shoes or rubber-soled shoes.
Back to topSee also the
temperatures month by month