Select units of measurement for the temperature and rainfall tables (metric or imperial).
Average weather, temperature, rainfall, sunshine
In Afghanistan, a country in south-central Asia, there is usually an
arid continental climate, with cold, relatively rainy winters (and a rainy peak in spring) and hot, sunny summers. However, there are substantial differences depending on area and altitude: the south is desert, many areas are rather cold because of altitude, and the far east is relatively rainy even in summer, since it is partly affected by the Indian monsoon.
Precipitation (rain or snow) is generally scarce, at semi-desert or desert levels, except in the eastern regions, where it exceeds in some areas 500 millimeters (20 inches) per year, while in the far east, near the border with Pakistan (Kunar and Nurestan provinces), it even reaches 1.000 mm (40 in).
During winter, the center-north of the country (and more rarely the south) is reached by
disturbances of Mediterranean origin, which bring a bit of rain, and even
snow, more likely in the mountains.
In early spring, when the southern Asian landmass starts to warm up, the clash between air masses becomes stronger, so rainfall increases; in fact, March is often the wettest month.
Later, the rains decrease, and from June to September, it usually never rains. Only in the easternmost region, east of Kabul, owing to the last offshoot of the monsoon that affects India and Pakistan, there is a certain increase in rainfall in July and August.
Summer is dry and sunny, very hot up to high altitudes.
Index
Northern plains
In the
northern plains, the ancient Bactria (see Mazar-i-Sharif), crossed by the Amu Darya River, which marks the border with the former Soviet republics, the climate is continental, with quite cold winters (but the average daily temperature exceeds freezing also in January) and very hot summers. In winter, however, cold waves are possible, with peaks of -20 °C (-4 °F). Summer is very hot, with peaks of 45 °C (113 °F) and even more, and sunny.
Mazar-i-Sharif
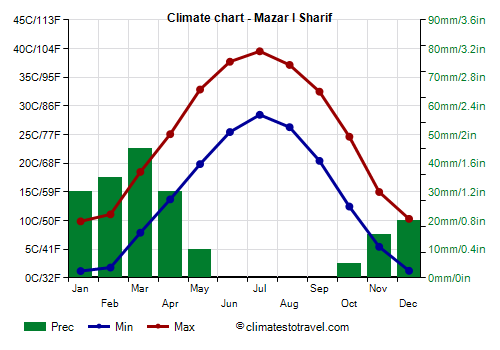
In
Mazar-i-Sharif, located at 360 meters (1,200 feet) above sea level, the average temperature ranges from 5.5 °C (42 °F) in January to 34 °C (93 °F) in July.
Precipitation is scarce and occurs in winter and spring, with a maximum in March, when the clash between air masses can sometimes cause strong winds as well.
North-central
Afghanistan is a
mountainous country, and it's crossed by the range of
Hindu Kush in its various chains, but also by the Pamir in the far north-east, in the frigid Wakhan Corridor, near the border with China. Many cities, starting from the capital, are located in narrow valleys, shaped by rivers between the mountains, at higher or lower elevations. In the country, there are many very high peaks, among which Noshaq, 7,492 meters (24,580 feet) high, Shar Dhar, 7,038 meters (23,090 ft), and Lunkho e Dosare, 6,901 meters (22,641 ft), all three at the border with Pakistan; we can also mention Kohe Bandaka, 6,843 meters (22,451 ft), which is 25 km (15 mi) away from the border with Pakistan. At high altitudes, above 4,000 meters (13,000 feet), there are vast glaciers.
Bamyan
In
Bamyan, situated at 2,500 meters (8,200 feet) above sea level, 125 km (77 miles) north-west of Kabul, winter is freezing, and although the temperature rises quite a bit in summer, nights are still very cool or even cold.
West of Bamyan, and at 3,000 meters (10,000 feet) above sea level, we find the six lakes of Band-i-Amir, protected in a national park.
Kabul
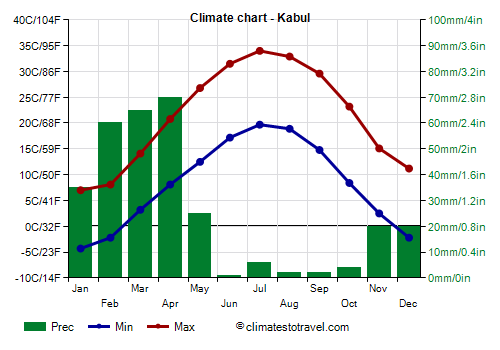
The capital,
Kabul, is located at a high altitude as well, 1,800 meters (5,900 feet) above sea level. Winter is cold, with an average temperature in January of 1.5 °C (34.5 °F), with nights normally below freezing. Sometimes there can be cold spells, with lows of -15 °C (5 °F) or even below. Snowfalls are quite frequent and sometimes abundant.
Summer is very hot, dry and sunny.
Precipitation in Kabul is quite scarce and amounts to 300 mm (12 in) per year. The rainiest season is spring. In summer it almost never rains.
In Kabul the sun shines quite often even in winter, while in summer it shines regularly.

Jalalabad
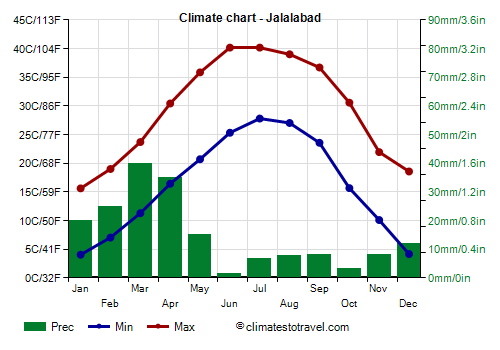
East of Kabul,
Jalalabad, protected by the mountains to the north and close to Pakistan (it is located 60 km or 37 mi away from the Khyber Pass), has a decidedly milder winter than the capital, so much so that the average in January is close to 10 °C (50 °F).
In the west (see
Herat), summer is characterized by an intense and frequent wind that blows from the north, the "wind of one hundred and twenty days" (
Bad-i-Sad-u-Bist-Ruz), from June to September, raising sand, dust, and salt.
South
Kandahar
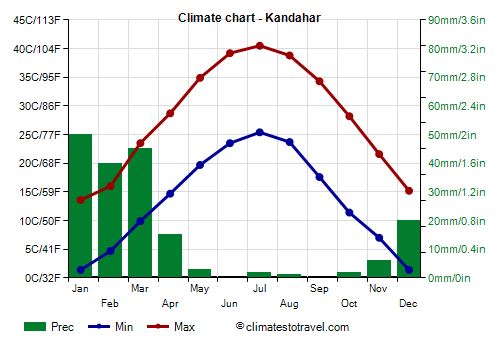
In southern Afghanistan, roughly starting from the Farah-
Kandahar line, the climate is warmer, and snowfalls in winter are rare.
Precipitation in Kandahar is decidedly low, as it does not reach 200 mm (8 in) per year. In practice, the only relatively rainy period is from January to March.
In Kandahar the sun shines frequently all year round, but especially in the long hot and dry period from May to October.
South of Kandahar, there is a wide
desert area (regions of Sistan and Baluchistan), occupied by a plateau at an average altitude of 500/700 meters (1,600/2,300 feet) in the western part, where we find the Dasht-e-Margo ("desert of death"), and between 700 and 1,200 meters (2,300 and 4,000 feet) in the eastern part, where we find the Rigestan Desert. In the middle, the Helmand River flows, along which some cities are found. Rainfall drops to around 80/100 mm (3.1/4 in) per year in the northern part and as low as 45/50 mm (1.8/2 in) in the southern part.
When to go
The best times to visit Afghanistan are
spring and autumn, to avoid both the winter cold and the summer heat, generally, the months of April and October (and even March and November in the southern deserts). However, in these months, it can get hot during the day and cold at night. Autumn is preferable because it is drier and less windy.
You can visit the
mountainous areas above 2,000 meters (6,500 feet) in summer, which is definitely the best season at the highest altitudes (since in the rest of the year the cold dominates).
What to pack in the suitcase
In
winter: for Kabul and the mountains, bring very warm clothes, such as a down jacket, a hat, a scarf, gloves; for the plains of the north and Herat, you can add a lighter jacket for mild days; for Farah and Kandahar, warm clothes, such as a sweater, a coat, and a hat; for the deserts of the south, a sweater, a jacket, a warm jacket for the night, and a scarf for the sand.
In
summer: for the plains of the north and the main cities of the plateau, bring lightweight clothing of natural fibers for the day, a hat for the sun, a desert turban, a sweatshirt for the evening. In Kabul, you can add a jacket for colder nights.
For the high mountains above 4,000 meters (13,000 feet), bring a down jacket, a hat, gloves, and a scarf.
For the Kunar Province, a raincoat or umbrella.
When visiting mosques, you must keep your shoulders and legs covered, and take off your shoes. Women should avoid low-cut dresses.
Climate data - Afghanistan
| Bamyan (2,600 meters) |
|---|
Bamyan, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | -10 | -6 | -4 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 4 | 0 | -5 | -9 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 1 | 2 | 8 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 26 | 26 | 23 | 17 | 11 | 5 |
|---|
| Precip. | 40 | 55 | 75 | 80 | 55 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 25 | 35 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 5 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 6 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 3 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Farah (750 meters) |
|---|
Farah, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 2 | 5 | 9 | 15 | 20 | 26 | 27 | 25 | 20 | 12 | 7 | 3 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 14 | 16 | 22 | 29 | 36 | 41 | 43 | 40 | 37 | 29 | 23 | 17 |
|---|
| Precip. | 25 | 25 | 20 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 10 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Feyzabad (1,200 meters) |
|---|
Feyzabad, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | -5 | -4 | 3 | 9 | 12 | 16 | 18 | 18 | 13 | 9 | 3 | -3 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 7 | 9 | 18 | 26 | 29 | 34 | 37 | 38 | 32 | 27 | 18 | 11 |
|---|
| Precip. | 55 | 75 | 105 | 105 | 75 | 10 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 35 | 45 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 4 | 7 | 11 | 13 | 11 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Herat (900 meters) |
|---|
Herat, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | -1 | 1 | 7 | 11 | 17 | 22 | 24 | 22 | 16 | 9 | 4 | 0 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 10 | 13 | 19 | 25 | 32 | 36 | 38 | 36 | 32 | 26 | 17 | 12 |
|---|
| Precip. | 50 | 45 | 55 | 30 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 35 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 6 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 5 |
|---|
|
|
| Sun hours | 5 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 5 |
|---|
|
| Jalalabad (580 meters) |
|---|
Jalalabad, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 4 | 7 | 11 | 16 | 21 | 25 | 28 | 27 | 24 | 16 | 10 | 4 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 16 | 19 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 40 | 40 | 39 | 37 | 31 | 22 | 19 |
|---|
| Precip. | 20 | 25 | 40 | 35 | 15 | 0 | 5 | 10 | 10 | 5 | 10 | 10 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 4 | 5 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|
|
|
| Sun hours | 6 | 7 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 6 |
|---|
|
| Kabul (1,800 meters) |
|---|
Kabul, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | -4 | -2 | 3 | 8 | 12 | 17 | 20 | 19 | 15 | 8 | 2 | -2 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 7 | 8 | 14 | 21 | 27 | 32 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 23 | 15 | 11 |
|---|
| Precip. | 35 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 25 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 20 | 20 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 5 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
|---|
|
|
| Sun hours | 6 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 6 |
|---|
|
| Kandahar (1,000 meters) |
|---|
Kandahar, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 1 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 24 | 25 | 24 | 18 | 11 | 7 | 1 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 14 | 16 | 24 | 29 | 35 | 39 | 40 | 39 | 34 | 28 | 22 | 15 |
|---|
| Precip. | 50 | 40 | 45 | 15 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 20 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 4 | 5 | 6 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
|---|
|
|
| Sun hours | 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 7 |
|---|
|
| Kunduz (400 meters) |
|---|
Kunduz, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | -2 | 0 | 6 | 12 | 16 | 21 | 23 | 22 | 16 | 11 | 4 | 0 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 6 | 10 | 16 | 23 | 30 | 37 | 39 | 37 | 32 | 24 | 16 | 10 |
|---|
| Precip. | 45 | 55 | 75 | 55 | 30 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 25 | 30 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 5 | 6 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 6 |
|---|
|
|
| Sun hours | 4 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 11 | 10 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 4 |
|---|
|
| Lashkar Gah (780 meters) |
|---|
Lashkar Gah, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 1 | 3 | 8 | 14 | 17 | 21 | 23 | 20 | 14 | 9 | 4 | 1 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 14 | 17 | 23 | 30 | 36 | 41 | 42 | 40 | 36 | 30 | 22 | 17 |
|---|
| Precip. | 25 | 30 | 30 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 15 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 5 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 |
|---|
|
|
| Sun hours | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 11 | 9 | 8 | 7 |
|---|
|
| Mazar I Sharif (360 meters) |
|---|
Mazar I Sharif, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 1 | 2 | 8 | 14 | 20 | 25 | 28 | 26 | 20 | 12 | 5 | 1 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 10 | 11 | 18 | 25 | 33 | 38 | 40 | 37 | 32 | 25 | 15 | 10 |
|---|
| Precip. | 30 | 35 | 45 | 30 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 15 | 20 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 4 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
|---|
|
|
| Sun hours | 4 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 10 | 12 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 4 |
|---|
|
| North Salang (3,365 meters) |
|---|
North Salang, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | -13 | -14 | -10 | -3 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 1 | -3 | -8 | -10 |
|---|
| Max temp. | -6 | -5 | -2 | 4 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 14 | 11 | 6 | 2 | -3 |
|---|
| Precip. | 110 | 140 | 185 | 200 | 125 | 10 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 30 | 70 | 105 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 13 | 15 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 9 | 11 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Zaranj (475 meters) |
|---|
Zaranj, location on the map |
|---|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 0 | 3 | 8 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 27 | 25 | 18 | 12 | 5 | 1 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 14 | 19 | 25 | 33 | 37 | 43 | 42 | 41 | 37 | 31 | 23 | 18 |
|---|
| Precip. | 20 | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
See also the
temperatures month by month