Select units of measurement for the temperature and rainfall tables (metric or imperial).
Average weather, temperature, rainfall, sunshine
In Nepal, there are different climates according to altitude: the
sub-tropical climate with a rainy season in the southern flat strip, the temperate climate in the low mountains, and finally, the cold mountain climate in the peaks of the Himalayas.
Rainfall is abundant in the period of the
summer monsoon (June to early October), which, however, penetrates with difficulty in some sheltered inland valleys and on the northern slopes. On the southern slopes, at equal altitude, the east is rainier than the west.
The climate in detail
The plain
In the thin
southern plain, a region known as
Terai (see Dhangadhi, Siddharthanagar, Nepalganj, Birganj, Janakpur, Biratnagar), the climate is that of the Indo-Gangetic plain, which is also found in northern India. In winter, it's sunny and mild, pleasantly warm during the day but cool at night, sometimes even cold. The average temperatures in January is around 15 °C (59 °F). Sometimes fog can form.
By March, the temperature rises considerably and it begins to be hot, while
from April to June it's scorching hot, and highs can reach or exceed 40 °C (104 °F).
In June, the
summer monsoon arrives, characterized by heavy rains, in the form of downpours and thunderstorms. The monsoon arrives first in the east, in early June, while in the west it comes in the middle of the month or so. The temperature decreases, with the maximum dropping to around 33 °C (91 °F) in July and August, but the humidity increases, making the heat muggy.
Rainfall ranges from 1,400 to 1,800 millimeters (55 to 70 inches) per year, and is intense especially in July and August, when it exceeds 300 mm (12 in) per month, but in certain areas at the foot of the mountains, especially in the east of the country, it can exceed 600 mm (23.5 in) per month.
Nepalganj
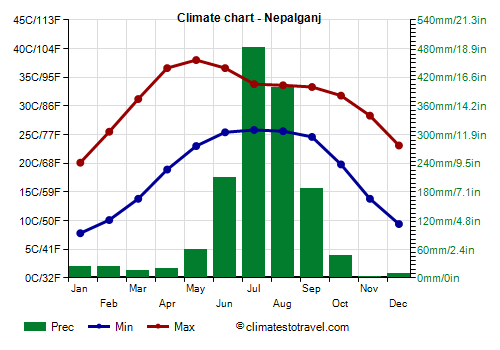
In Nepalganj (or Nepalgunj), located in the southwest near the border with India, in
winter, from mid-November to late February or early March, nights are cool, and sometimes even cold. In January 2013, the temperature dropped to 0 °C (32 °F).
In addition, from November to February,
fog can form at night and in the early morning. The fog usually dissolves during the day, however, in these situations, it can sometimes be cool even during the day, with highs of 14/15 °C (57/59 °F), and sometimes even below.
From mid-March to mid-June, before the monsoon, it is
very hot. The temperature reached 45 °C (113 °F) in June 1995.
The monsoon starts to withdraw by early October in the west, and about a week later in the east. The weather returns to be sunny, and even though October is still a hot month, the humidity decreases and the night temperature becomes a bit cooler.
In the
easternmost part of the flat area (see Biratnagar), the increase in temperature in the period from March to June is limited, in fact, the average maximum temperature does not go above 33/34 °C (91/93 °F) in April and May. Here, already in the second half of April, the first afternoon thunderstorms occur, prior to the arrival of the monsoon itself.
The Himalayas
Above 800/1,000 meters (2,600/3,300 feet), the climate is temperate, while the rainfall pattern is the same.
Pokhara
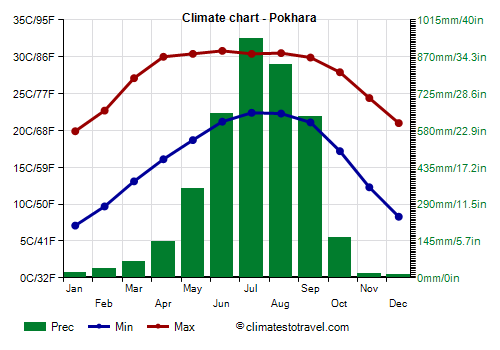
In
Pokhara, at 800 meters (2,600 feet), the average temperature ranges from 13.5 °C (56 °F) in January to 26 °C (79 °F) in July and August.
In winter, the temperature can drop to around 0 °C (32 °F) on colder nights. Sometimes fog can form. During the day, temperatures are very similar from April to September.
The highest temperatures of the year typically occur before the monsoon, in May and sometimes in April, albeit for short periods.
Pokhara is
the rainiest city of Nepal because it is located at the foot of the Annapurna Range, where the southern currents that prevail in summer are forced to rise when they encounter the mountain slopes. In fact, rainfall amounts to 3,900 mm (153 in) per year, including up to 940 mm (37 in) in July and 840 mm (33 in) in August.
However, here too in winter the rains are rare, but there can be some atmospheric instability already in spring, with significant thunderstorms in April and May.
Kathmandu
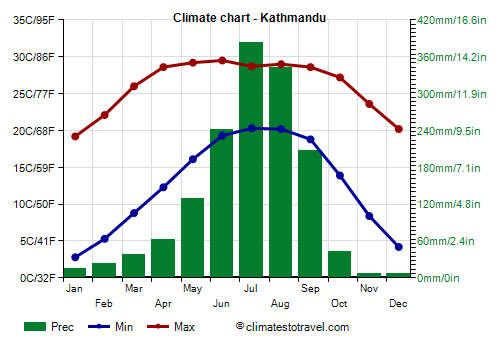
In the capital,
Kathmandu, at 1,400 meters (4,600 feet) above sea level, the climate is mild.
The average January temperature is around 11 °C (51.5 °F), but the temperature range is high, so
it gets cold at night, while during the day the sun makes the air mild. Sometimes the temperature can drop as low as 0 °C (32 °F) or slightly below. The coldest record is -3.5 °C (25.7 °F) and was set in January 1978. Also, fog can form at night.
Summer is hot, with highs around 27/29 °C (81/84 °F) for a long period, from April to October. Generally, the highest temperatures of the year are recorded before the monsoon, in May and sometimes in April, with highs of around 35 °C (95 °F).
Annual
rainfall amounts to 1,500 mm (59 in), of which 130 mm (5.1 in) fall already in May (due to thunderstorms that precede the monsoon), and up to 385 mm (15 in) in July, which is the rainiest month. In September, still 205 mm (8 in) of rain fall, and 45 mm (1.8) in October, concentrated in the first part of the month, before the monsoon withdraws.
In Kathmandu, and in Nepal in general, the
sun shines quite often in winter and very often in spring, before the monsoon. In contrast, in the rainy season, especially from July to September, the sky is often cloudy, so it's difficult to spot the highest mountains of the Himalayas.

Going up in altitude, both temperature and rainfall vary with altitude. In theory, they also vary with slope exposure, however, since most of the mountains of Nepal are situated on the
southern side, the temperature is relatively mild even at high altitudes. However, above 2,000 meters (6,500 feet), in winter, the temperature often drops below freezing at night.
Jumla
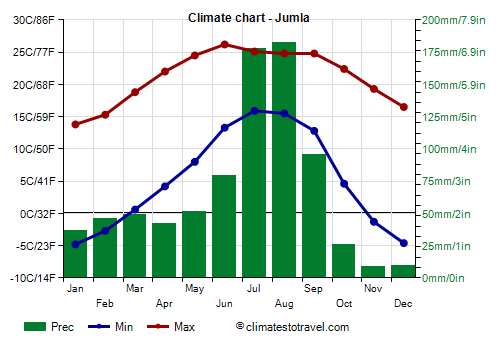
In
Jumla, located at 2,300 meters (7,500 ft), the average in January is 4.5 °C (40 °F), but with a strong temperature range, so the minimum temperatures drop to almost -5 °C (23 °F).
In the areas closed between the mountains, the summer monsoon penetrates with more difficulty. In Jumla, only 805 mm (31.7 mm) of rain fall per year.
Namche Bazaar
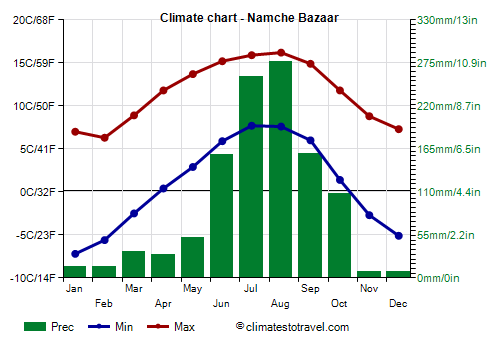
At higher altitudes, it gets even colder. In
Namche Bazaar, located at 3,450 meters (11,300 ft) above sea level, the average in January is 0 °C (32 °F), while that of July and August is 12 °C (53.5 °F).
Precipitation amounts to 1,100 mm (44 °F) per year. Even though the winter is dry, it can sometimes snow.
Some particularly sheltered inland valleys receive an even lower amount of rainfall, and have a desert or semi-desert landscape, such as the kingdom of
Mustang, which is located in an arid valley north of the massifs of Annapurna and Dhaulagiri.
Highest peaks
Going up in altitude, usually, the average temperature in January drops below freezing (0 °C or 32 °F) above 3,000 meters (9,800 ft). Above 3,600 meters (11,800 ft), the
subpolar climate zone begins, that is, where the average temperature of the warmest month does not exceed 10 °C (50 °F).
The
perennial snows in Nepal are found at very high altitudes, around 6,000 meters (20,000 feet).
 Everest, where is located
Everest, where is located
In Nepal, some of the
highest mountains on Earth are found: Mount
Everest is the highest, with its 8,848 meters (29,029 feet), on the border with China. The only mount outside Nepal is
K2, which is located in the northwest, on the border between China and Pakistan.
The other highest mountains in Nepal are:
Kanchenjunga, the third highest mountain in the world, 8,586 meters (28,169 feet), on the border with the Indian state of Sikkim;
Lhotse, the fourth, 8,516 meters (27,940 feet), located just 3 kilometers (2 miles) south-east of Mount Everest and still on the border with China;
Makalu, the fifth, 8,481 meters (27,766 feet), 20 km (12 mi) south-east of Mount Evererst and still on the border with China;
Cho Oyu, the sixth, 8,201 meters (26,906 feet), 28 km (17 mi) north-west of Mount Everest and still on the border with China;
Dhaulagiri, the seventh, located in the interior of Nepal and not at the border, 8,167 m (26,795 ft);
Manaslu, the eighth, 8,156 m (26,759 ft), and
Annapurna, the ninth, 8,091 m (26,545 ft).

At the
base camp of Mount Everest, in the Khumbu glacier, 5,300 meters (17,400 ft) above sea level, only 450 mm (17.5 in) of rain or snow fall per year. Here, the average temperature is around -18 °C (0 °F) in January and -2 °C (28 °F) in July, while at the Everest's summit it's around -36 °C (-33 °F) in January and -18 °C (0 °F) in July. On the highest peaks of Nepal, terrible wind storms occur, especially in winter.
Tropical cyclones
Nepal is too far from the sea to be directly hit by tropical cyclones, but the
remains of cyclones affecting India, which usually come from the Bay of Bengal, can cause heavy rains in the Nepalese plains as well as snow in the mountains.
For example, on October 14, 2014, heavy snowfalls caused avalanches in the Annapurna and Dhaulagiri areas, as a result of the approach of the remains of Cyclone Hudhud.
In order to avoid these accidents, it is advisable to consult the weather forecasts and the official warnings, as well as to rely on local expert guides.
Cyclones typically occur from mid-April to early December, but they are most likely in May-June and October-November.
When to go
The best time to visit Nepal in its entirety runs from
November to February, to avoid the summer monsoon but also the heat of the plains, which is intense from March to October.
If you want to visit Kathmandu, and especially if you want to go
trekking in the mountains, you may choose
spring and autumn, especially in March and April, and from mid-October to mid-November, ie the periods when it is possible to avoid the winter cold as well as the mud due to summer rains. Autumn is the best period, since it is the least rainy, in addition, the atmosphere is particularly transparent, to the point that you can see the snow-capped mountains at great distances.
If you want to go hiking in a
snowy landscape, you have to go in
winter and above 3,000 meters (10,000 feet), though being that it's a dry season, it is not guaranteed that in a given period it snows. Occasionally, around this altitude it can also snow in spring and autumn. To be sure to see the snow, you have to go to the base camp of Everest or Annapurna, which, however, can only be reached after days of trekking.
In Kathmandu, even though the winter nights are cold, it practically never snows. However, in winter, it can sometimes snow on the Shivapuri national park, at 2,400 meters (7,800 ft) above sea level and north of Kathmandu, on Mount Phulchowki, at 2,700 meters (8,900 ft) and south of the city, or in Daman, at 2,300 meters (7,500 feet) and south-west of the city.
It snows more often in Kalinchok, located at 3,400 meters (11,000 feet) near Kathmandu, and a bit more rarely in Ghorepani, located at 2,800 meters (9,200 feet) near Pokhara and at the foot of Annapurna.
In general, expeditions for Mount
Everest and the other highest peaks are organized in two periods, from May 20th to June 5th, and from October 1st to October 20th. In these two periods, the temperature on the summit of Mount Everest is around -25/-27 °C (-13/-17 °F), and it's possible to take advantage of the only two favorable periods, between the cloudiness and the snowfalls that occur in summer and the wind storms that occur in winter. However, in high mountains, the weather can vary greatly depending on meteorological situation, so it's better to check the forecast for the following days, and in any case, to rely on expert guides.
What to pack
In
winter: in the plains, bring spring/autumn clothes (light for the day), a jacket and a sweater for the evening. In Kathmandu and Pokhara, spring/autumn clothes for the day, warm for the evening, a jacket, a hat, a scarf, sunglasses, sunscreen. Above 2,000 meters (6,500 feet), warm winter clothes, a down jacket, hiking shoes. At higher altitudes, outfit for the big cold, synthetic, thermal long underwear, gloves, a parka, a hat, a scarf.
In
summer: for the plains, bring lightweight clothing of natural fibers, a light raincoat or umbrella. In Kathmandu and Pokhara, light clothing, a sweatshirt for the evening, a raincoat or umbrella. Above 2,000 meters (6,500 feet), spring/autumn clothes, a sweater and a jacket for the evening. At the highest altitudes, a fleece, a wind jacket, a down jacket, a hat, gloves, a scarf. A sleeping bag and a warm jacket for outdoor overnight stays.
Climate data - Nepal
| Biratnagar |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 9 | 12 | 16 | 21 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 21 | 16 | 11 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 22 | 26 | 31 | 34 | 34 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 32 | 30 | 25 |
|---|
| Precip. | 10 | 10 | 15 | 60 | 170 | 305 | 475 | 355 | 270 | 75 | 5 | 5 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 1 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 10 | 15 | 19 | 16 | 14 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Birgunj |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 8 | 10 | 14 | 19 | 23 | 25 | 26 | 26 | 24 | 20 | 14 | 10 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 21 | 26 | 31 | 35 | 35 | 34 | 33 | 33 | 33 | 32 | 29 | 24 |
|---|
| Precip. | 15 | 15 | 15 | 40 | 135 | 275 | 550 | 420 | 260 | 70 | 5 | 10 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 9 | 13 | 19 | 16 | 12 | 3 | 0 | 1 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Ghorahi (665 meters) |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 6 | 9 | 13 | 18 | 21 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 21 | 16 | 11 | 7 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 21 | 24 | 29 | 33 | 34 | 33 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 29 | 26 | 22 |
|---|
| Precip. | 20 | 25 | 20 | 30 | 90 | 250 | 420 | 430 | 235 | 50 | 5 | 5 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 7 | 14 | 22 | 21 | 15 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Jomsom (2,745 meters) |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | -2 | -1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 14 | 14 | 12 | 6 | 2 | -1 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 10 | 12 | 15 | 19 | 21 | 23 | 23 | 23 | 21 | 18 | 15 | 12 |
|---|
| Precip. | 15 | 20 | 30 | 20 | 20 | 30 | 45 | 45 | 35 | 20 | 5 | 5 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 2 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 9 | 6 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Jumla (2,300 meters) |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | -5 | -3 | 1 | 4 | 8 | 13 | 16 | 16 | 13 | 5 | -1 | -5 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 14 | 15 | 19 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 25 | 25 | 25 | 22 | 19 | 16 |
|---|
| Precip. | 35 | 45 | 50 | 40 | 50 | 80 | 180 | 180 | 95 | 25 | 10 | 10 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 4 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 9 | 11 | 21 | 21 | 13 | 3 | 1 | 1 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
| Kathmandu (1,400 meters) |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 3 | 5 | 9 | 12 | 16 | 19 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 14 | 8 | 4 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 19 | 22 | 26 | 29 | 29 | 30 | 29 | 29 | 29 | 27 | 24 | 20 |
|---|
| Precip. | 15 | 25 | 40 | 65 | 130 | 240 | 385 | 345 | 210 | 45 | 5 | 10 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 2 | 3 | 4 | 7 | 12 | 17 | 23 | 23 | 15 | 4 | 0 | 1 |
|---|
|
|
| Sun hours | 6 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 6 |
|---|
|
| Namche Bazaar (3,450 meters) |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | -7 | -6 | -2 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 1 | -3 | -5 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 7 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 15 | 12 | 9 | 7 |
|---|
| Precip. | 15 | 15 | 35 | 30 | 50 | 160 | 255 | 275 | 160 | 110 | 10 | 10 |
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
| Nepalganj |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 8 | 10 | 14 | 19 | 23 | 25 | 26 | 26 | 25 | 20 | 14 | 9 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 20 | 26 | 31 | 37 | 38 | 37 | 34 | 34 | 33 | 32 | 28 | 23 |
|---|
| Precip. | 25 | 25 | 15 | 20 | 60 | 210 | 485 | 395 | 185 | 45 | 5 | 10 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 5 | 10 | 19 | 18 | 11 | 2 | 0 | 1 |
|---|
|
|
| Sun hours | 7 | 8 | 8 | 10 | 9 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 | 7 |
|---|
|
| Pokhara (800 meters) |
|---|
|
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|
| Min temp. | 7 | 10 | 13 | 16 | 19 | 21 | 22 | 22 | 21 | 17 | 12 | 8 |
|---|
| Max temp. | 20 | 23 | 27 | 30 | 30 | 31 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 28 | 24 | 21 |
|---|
| Precip. | 20 | 35 | 65 | 140 | 355 | 650 | 940 | 840 | 635 | 160 | 15 | 10 |
|---|
| Prec. days | 2 | 4 | 6 | 10 | 18 | 22 | 26 | 24 | 19 | 8 | 1 | 1 |
|---|
|
|
| Sun hours | 7 | 7 | 8 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 6 |
|---|
|
See also the
temperatures month by month